1、点击layers→add data加载高程CAD
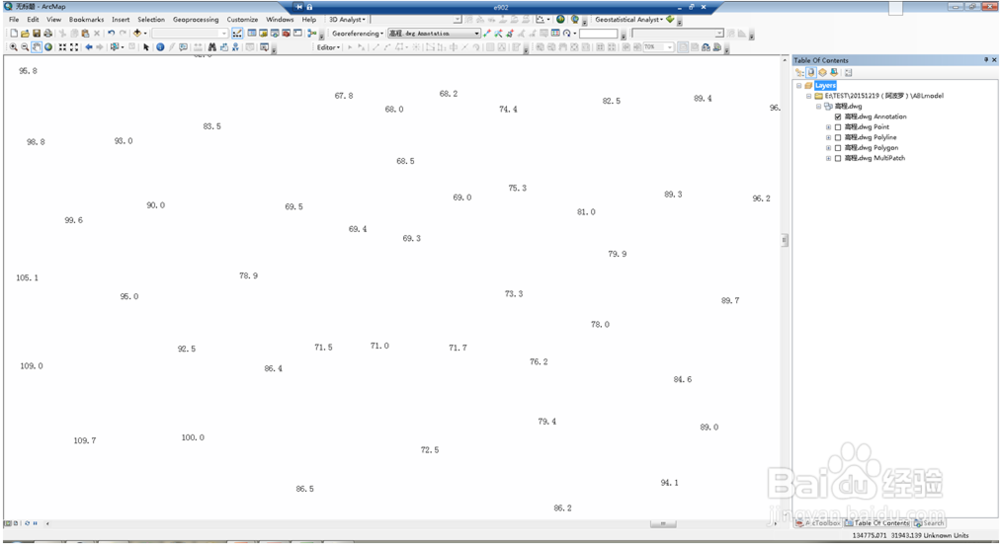
2、确定高程数据所在的层annotation,找到feature to point……将其转换为点shp文件。
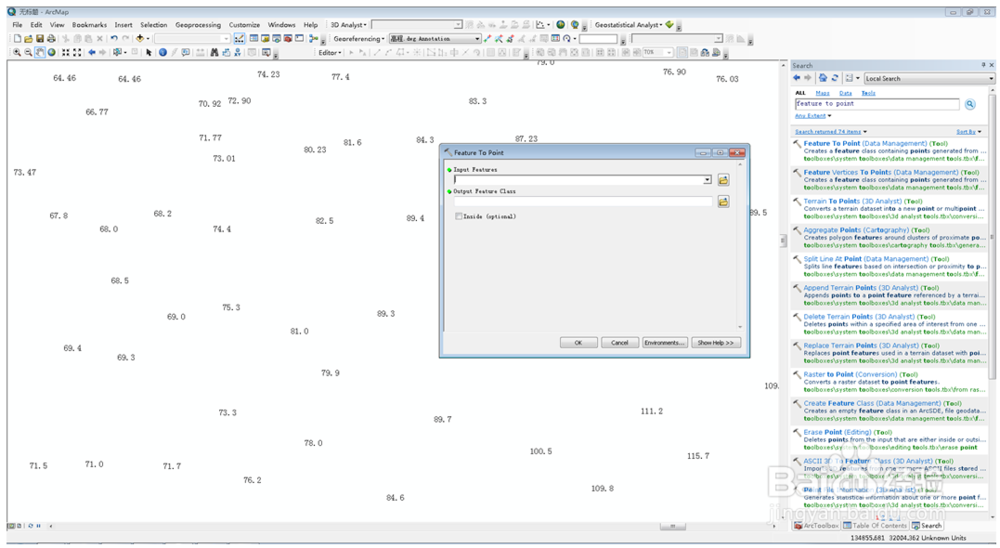
3、此时发现高程数据所在的列,类型为文本,应将其转换为数值格式。
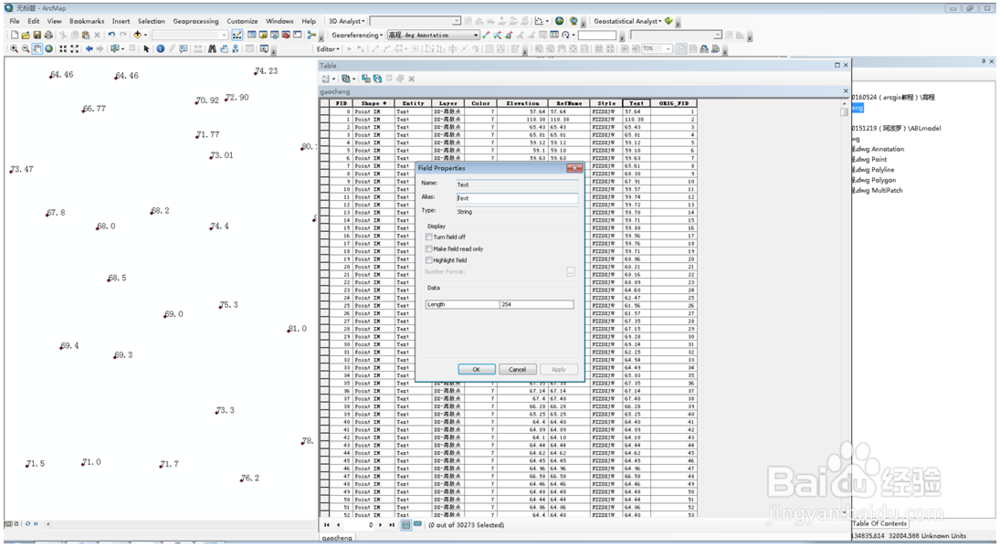
4、点击add field添加新的一列
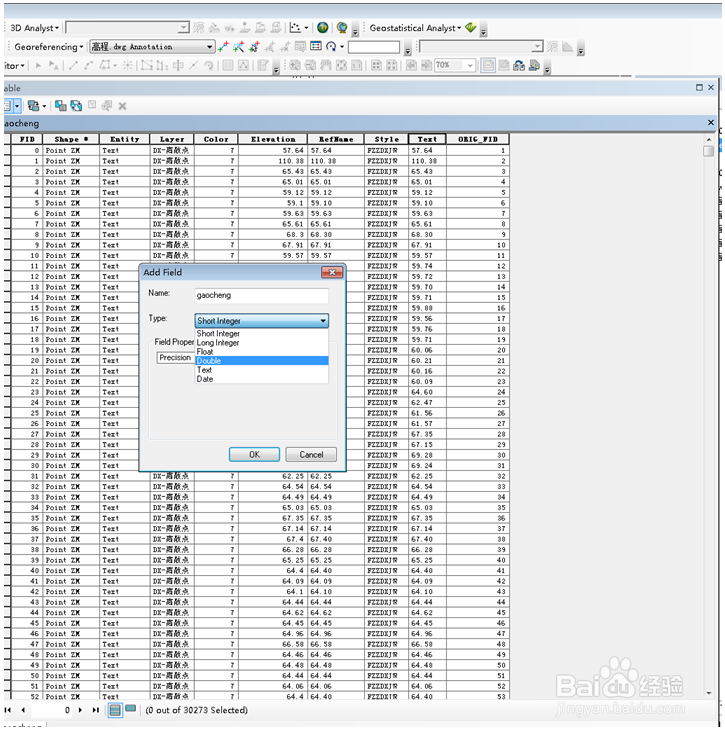
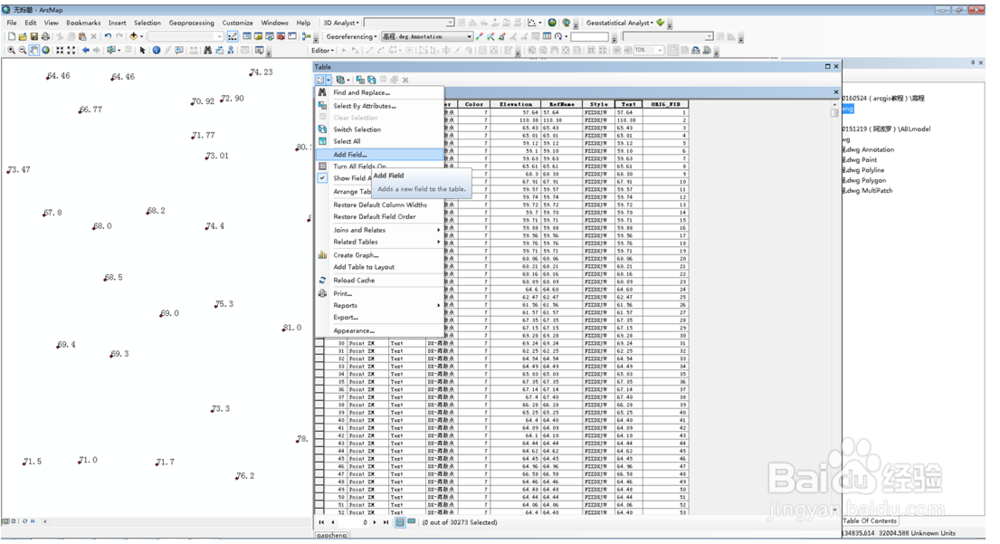
5、右键新添加的列,field calculator……
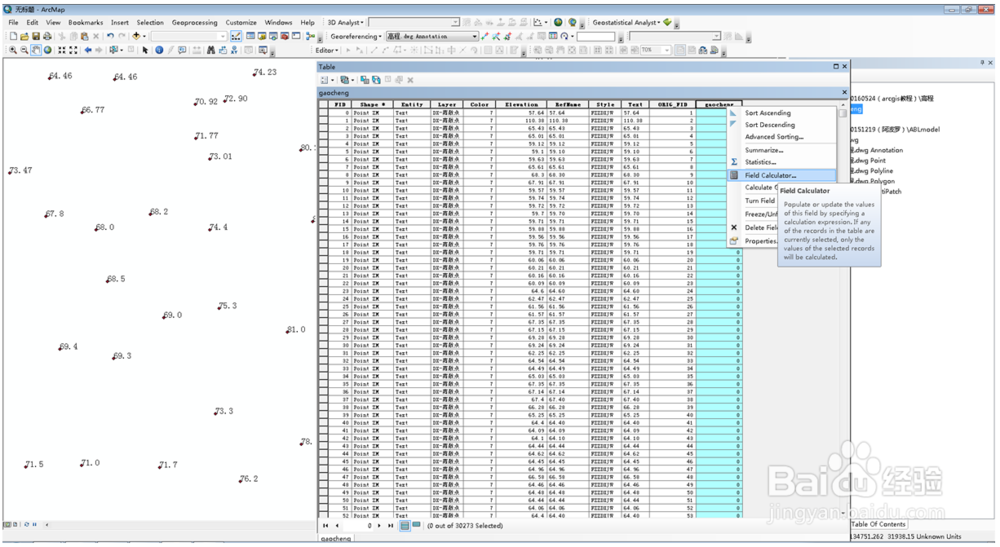
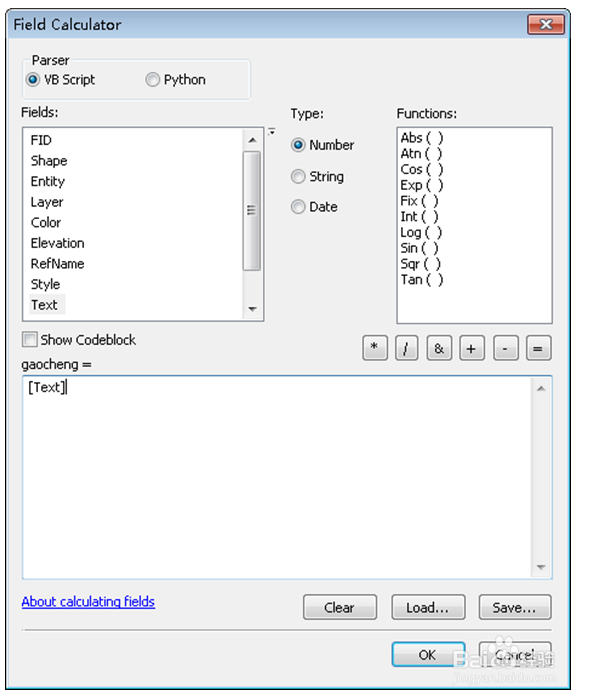
6、设置gaocheng=[Text]
7、这样就得到高程点的shp文件。将点高程转成面高程一般有两种操作:点高程转成TIN和点高程转成raster。首先,介绍点高程转成TIN。3D Analyst→ create TIN生成TIN文件。
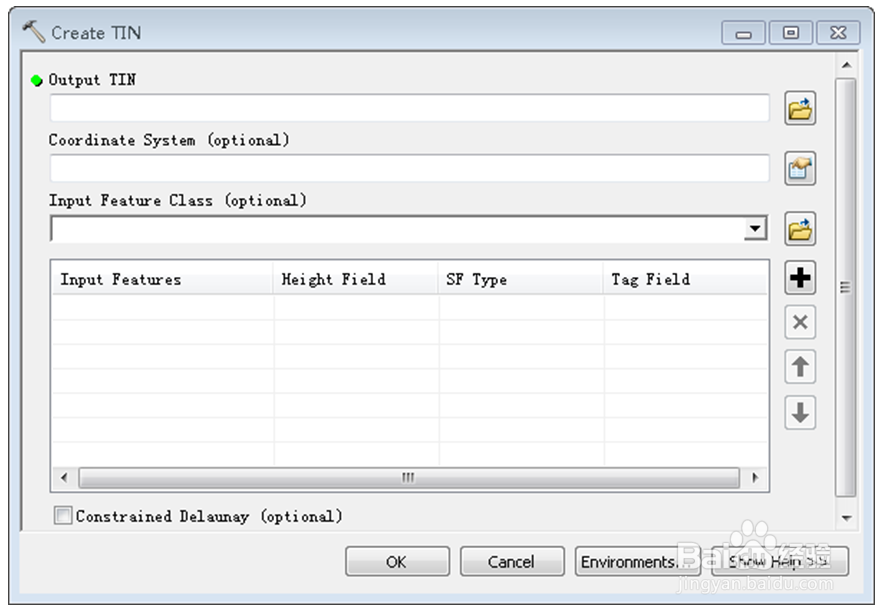
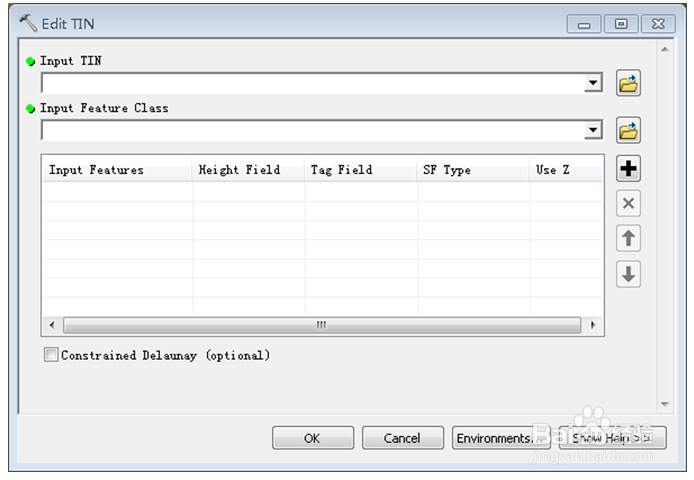
8、 Analyst→Edit TIN 可以对生成的TIN进行切割。Input feature class……中添加用来切割的多边形文件(shp)。
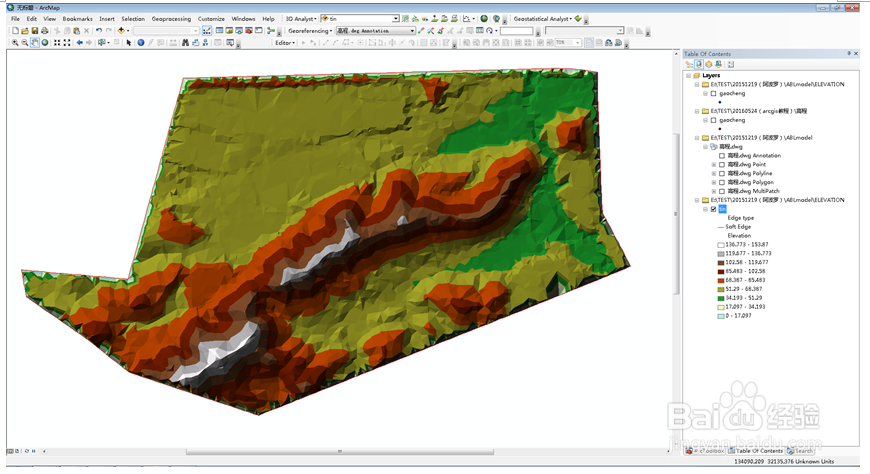
9、生成TIN文件的原始高程可以是等高线或高程点,或两者都有。其次,介绍点高程文件转为raster。3D analyst→Rater Interpolation,选择插值的方法。
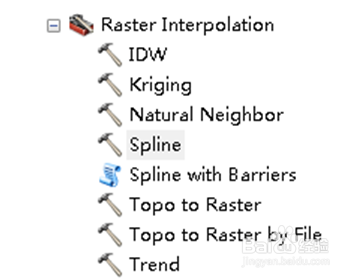
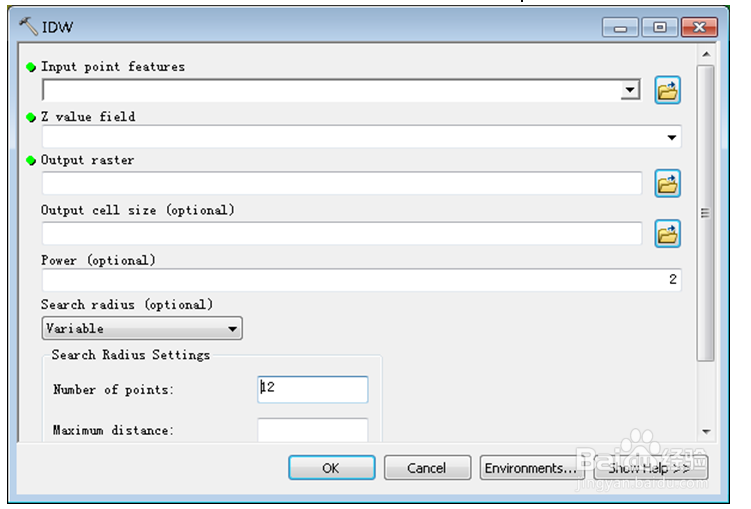
10、在“Output cell size …….”中确定插值栅格大小,一般有0.5m×0.5m、1m×1m、5m×5m、10×10m等。
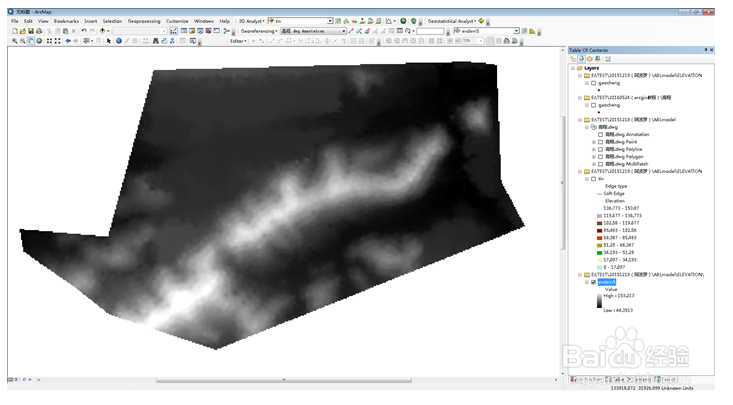
11、 analyst→raster surface→slope ……..,求栅格坡度。
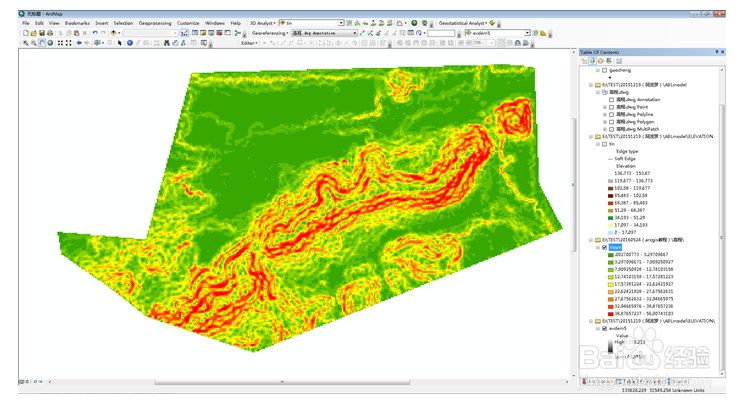
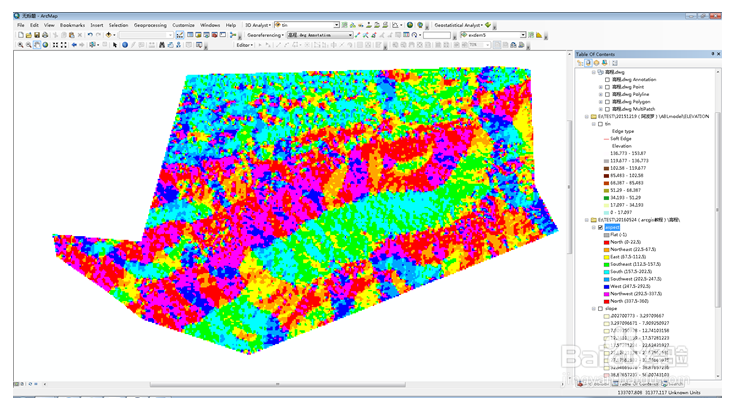
12、 analyst→raster surface→aspect ……..,求栅格度向。
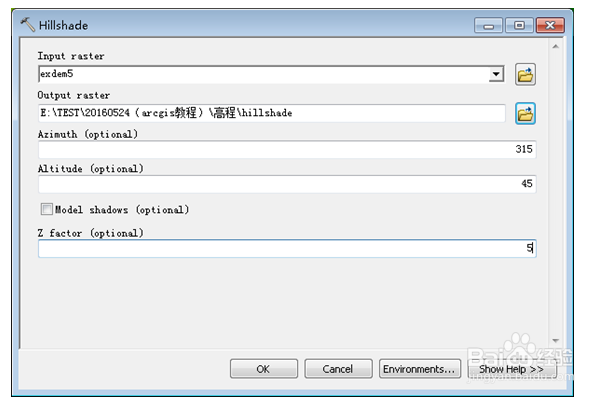
13、 analyst→raster surface→hillshade ……..计算山体阴影。
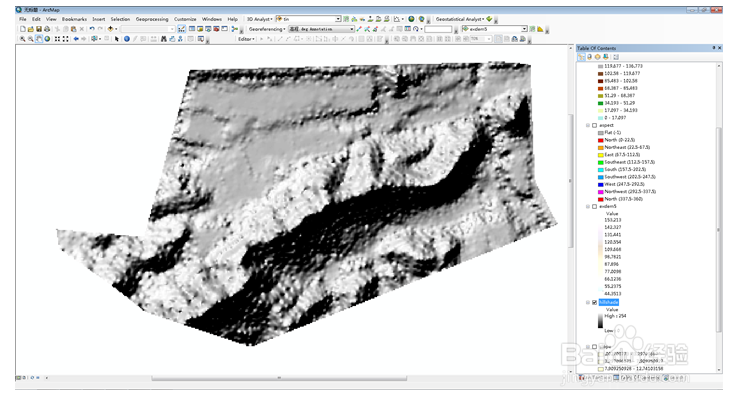
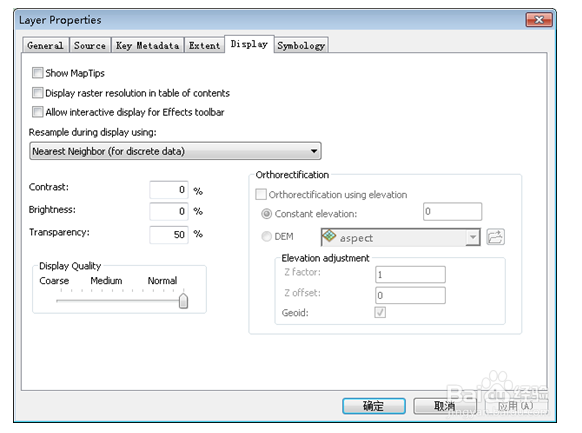
14、在layer中加载高程dem文件和hillshade文件,dem在上,hillshade在下。打开d髫潋啜缅em属性(layer properties)设置界面,设置显示图例、brigtness、transparency等。
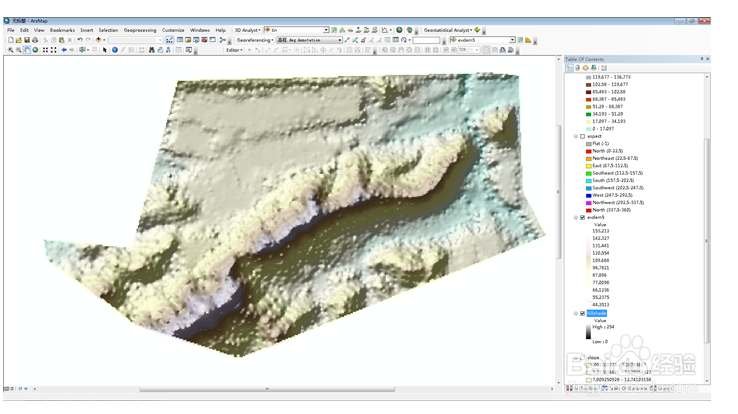
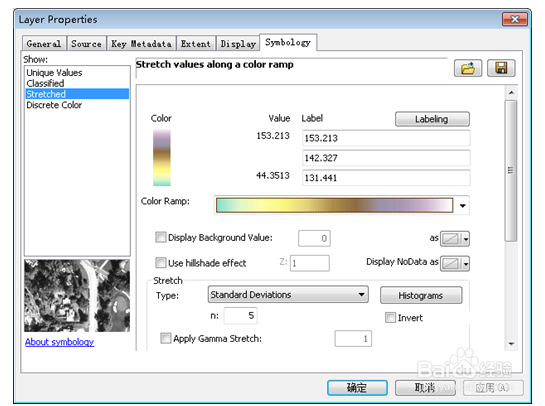
15、可以通过ArcGIS组件ArcScene进行三维渲染。步骤如下:陴查哉厥右键scene layer,添加高程dem,打开layer property,点击base heights进行自定义设置。
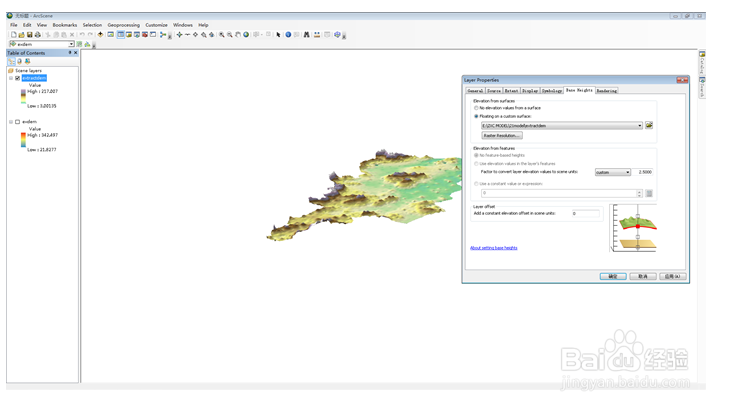
16、点击rendering,在“effects”选项卡中可以设置光角、光滑度等。